Logistics is an important component of supply chain management as it manages all the logistics processes, starting from planning, implementing, and controlling the storage and movement of raw materials, finished goods, and information from the manufacturer to the end users.
Other than delivering the goods and information from producer to consumer, there is one more type of logistics that is ruling the modern supply chain. It’s called Reverse Logistics.
Reverse logistics handles the exchange and return process of goods from the consumer to the supplier, warehouse, or manufacturer.
Let’s learn about this topic in detail in this comprehensive guide.
What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics optimizes the process of movement of finished goods from their final destination (consumers) to the point of origin (manufacturers, warehouses, suppliers).
The purpose of reverse logistics is to return, recycle, remanufacture, or dispose of the goods received from the customer. It also handles the recovery of the valuable material from the end-of-life products.
Essential Roles of Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics plays different roles in different industries involved in distribution networks, such as e-commerce, retail, and manufacturing. Let’s discuss its key roles:
1. E-commerce:
E-commerce handles the delivery of finished goods ordered by customers to their destination. In e-commerce, reverse logistics provides a logistics solution for returning or exchanging damaged goods received by customers, replacing them with fresh goods, and delivering them securely to the customers.
2. Retail:
Traditional retail stores also rely on reverse logistics to manage product returns. They need efficient systems to process returns, restock items, and handle defective goods to retain customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Manufacturing:
In manufacturing, it manages industrial waste and byproducts. This logistics process involves the recovery of scrap materials, defective parts, or used components for recycling or remanufacturing.
Examples
E-commerce –
Zappos offers a generous return policy that allows customers to return products for free within 365 days. This policy helps process these returns, restock items, and manage returned goods, which enhances customer satisfaction and supports brand loyalty.
Retail –
IKEA’s approach to reverse logistics includes managing returns and handling the disposal or recycling of returned products. The company’s commitment to sustainability involves refurbishing returned furniture and recycling materials, contributing to its environmental goals, and improving operational efficiency.
Manufacturing –
Dell’s Asset Recovery Services help businesses recycle or repurpose old IT equipment. Dell processes returned devices to recover valuable components and materials, minimizing environmental impact and supporting sustainability goals. This reverse logistics approach not only reduces waste but also provides economic benefits through the recovery of valuable resources.

Reverse Logistics vs. Forward Logistics
Forward logistics refers to the traditional flow of goods and services from the point of origin (such as a manufacturer or supplier) to the final destination (such as a retailer or end consumer). This process involves all the activities required to deliver products from production to consumption efficiently and effectively. Forward logistics encompasses the planning, execution, and management of this movement, ensuring that goods reach their intended destinations in the right quantities, at the right time, and in the right condition.
Traditional Role of Forward Logistics in the Supply Chain
Procurement and Supplier Management:
In forward logistics, the supply chain begins with the procurement of raw materials or components from suppliers. Effective supplier management ensures a steady flow of inputs needed for production.
Production and Manufacturing:
This phase entails turning raw components into finished products. Efficient production processes and scheduling are critical to meeting demand and maintaining inventory levels.
Warehousing and Inventory Management:
Before being delivered to retailers or consumers, finished goods are kept in warehouses. Inventory management involves maintaining optimal stock levels to balance supply and demand, reducing carrying costs, and preventing stockouts or excess inventory.
Order Processing and Fulfillment:
This involves handling customer orders, picking and packing products, and preparing them for shipment. Efficient order processing ensures timely and accurate fulfillment of customer requests.
Transportation and Distribution:
Products are transported from warehouses or manufacturing facilities to retailers or end consumers. Effective transportation management includes selecting appropriate shipping methods, optimizing routes, and managing logistics costs.
Customer Service and Support:
Forward logistics includes providing support to customers throughout the delivery process, addressing inquiries, and resolving any issues related to product delivery or order fulfillment.
Comparison of Reverse and Forward Logistics
Aspect | Forward Logistics | Reverse Logistics |
Flow Direction | Supplier to consumer. | Consumer to supplier. |
Primary Goal | Efficient delivery and distribution. | Efficient returns, recycling, and disposal. |
Main Activities | Procurement, production, warehousing, and distribution. | Returns processing, recycling, and remanufacturing. |
Inventory Management | Managing stock levels for demand. | Managing returned goods and recovery. |
Role in Sustainability | Efficiency in resource use. | Directly supports recycling and waste reduction. |
Customer Interaction | Focuses on order fulfillment and delivery. | Handles returns, refunds, and customer complaints. |
Examples | Shipping products to retailers or customers. | Processing returns or recycling electronic waste. |
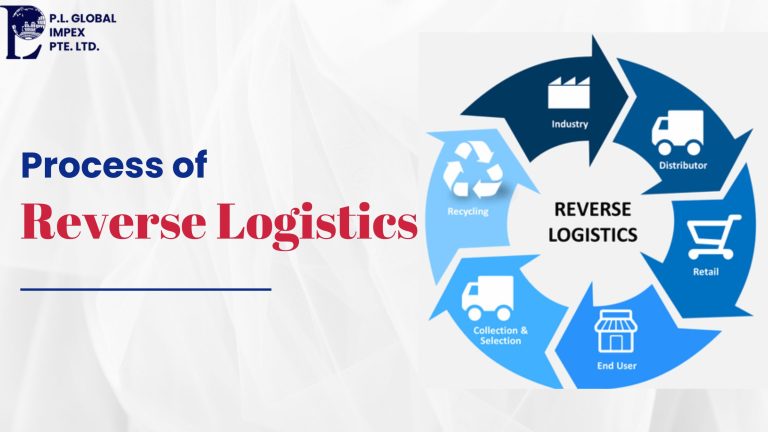
The Reverse Logistics Process
Reverse logistics involves managing the flow of goods from their final destination back to the point of origin or other destinations for return, recycling, remanufacturing, or disposal. Here are the key steps in the reverse logistics process:
1. Product Return:
- Customer Initiation: The process begins when a customer returns a product due to defects, dissatisfaction, or end-of-life.
- Return Authorization: The company authorizes the return, often requiring the customer to follow specific return procedures.
2. Return Processing:
- Product Inspection: Returned products are inspected for condition, usability, and adherence to return policies.
- Restocking: Products that are in good condition may be restocked and made available for resale.
3. Recycling:
- Material Recovery: Products that cannot be reused are dismantled, and valuable materials are recovered for recycling.
- Waste Management: Non-recyclable materials are managed according to environmental regulations.
4. Refurbishment/Remanufacturing:
- Repair and Refurbishment: Products that can be repaired or refurbished are restored to a sellable condition.
- Remanufacturing: Some products are fully remanufactured to meet original specifications or upgraded.
5. Disposal:
- Environmentally Responsible Disposal: Products that cannot be recycled or refurbished are disposed of in compliance with environmental regulations.
Reverse Logistics Cycle
Here’s a simplified map of the reverse logistics cycle from customer return to disposal:
1. Customer Return:
- Customer returns a product.
- Initiate return authorization.
2. Return Processing:
- Receive and inspect the returned product.
- Decide on restocking, refurbishing, or recycling.
3. Refurbishment/Remanufacturing:
- Repair or refurbish the product if feasible.
- Remanufacture if necessary.
4. Recycling:
- Dismantle and recover materials.
- Recycle valuable materials.
5. Disposal:
- Manage non-recyclable waste.
- Ensure compliance with disposal regulations.
Key Components
1. Product Return Policies:
- Guidelines outlining how returns are handled, including conditions for accepting returns and procedures for processing them.
- Importance: Ensures consistency and customer satisfaction and provides clear instructions for both customers and staff.
2. Tracking Systems:
- Systems are used to monitor the status and location of returned products throughout the reverse logistics process.
- Importance: Enhances visibility, improves efficiency, and allows for better management of returns and inventory.
3. Disposal Methods:
- Procedures for the final disposal of products that cannot be reused or recycled.
- Importance: Ensures compliance with environmental regulations and reduces the ecological impact of waste.
4. Third-Party Logistics Partnerships:
- Collaboration with external logistics providers who specialize in reverse logistics operations.
- Importance: Allows companies to leverage expertise, reduce operational costs, and improve efficiency in handling returns, recycling, and disposal.

The 5 Rs of Reverse Logistics
The 5Rs of reverse logistics manage the flow of products and materials from the end consumer back through the supply chain. Each “R” represents a key aspect of the reverse logistics process, which addresses different needs and objectives.
1. Returns:
The process of handling products that customers send back to the seller or manufacturer, usually due to defects, dissatisfaction, or incorrect orders.
Role in Reverse Logistics:
- Customer Satisfaction: Facilitates customer satisfaction by providing a mechanism for returning unwanted or faulty items.
- Inventory Management: Returned products are assessed for restocking or further processing, which helps in managing inventory levels.
- Refunds and Exchanges: Provides a structured approach to process refunds or exchanges, maintaining positive customer relations.
2. Recalls:
The process of retrieving products from the market due to safety issues, defects, or compliance problems.
Role in Reverse Logistics:
- Safety and Compliance: Ensures that defective or hazardous products are removed from circulation to protect consumer safety and adhere to regulations.
- Reputation Management: Helps manage and mitigate the impact on the company’s reputation by effectively handling recall situations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to legal and regulatory requirements for product safety and recall procedures.
3. Recycling:
The process of recovering valuable materials from products that are no longer in use and converting them into new materials or products.
Role in Reverse Logistics:
- Environmental Impact: Reduces waste and the environmental footprint by diverting materials from landfills and promoting sustainable practices.
- Resource Recovery: Recovers valuable raw materials (e.g., metals, plastics) that can be reused in manufacturing processes, conserving natural resources.
- Compliance: Meets regulatory requirements for waste management and recycling.
4. Repackaging:
Reconditioning or repackaging products to make them suitable for resale or further distribution.
Role in Reverse Logistics:
- Product Resale: Allows products that are in good condition but not in their original packaging to be repackaged and resold, often at a discounted price.
- Inventory Optimization: Helps in managing surplus or returned products by making them available for sale again, optimizing inventory levels.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces the need for new packaging materials and minimizes waste associated with packaging.
5. Repairs:
The process of fixing and restoring defective or damaged products to a usable condition.
Role in Reverse Logistics:
- Product Longevity: Extends the life of products by repairing and refurbishing them, which can be resold or returned to service.
- Cost Efficiency: Offers a cost-effective alternative to replacement by addressing issues through repair rather than disposal.
- Customer Retention: Enhances customer satisfaction by providing solutions for defective products, thus maintaining a positive relationship with customers.
How Reverse Logistics Impacts Supply Chain Management?
Reverse logistics significantly impacts overall supply chain management by influencing operations, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Here’s a detailed look at how reverse logistics affects the supply chain and its importance in driving competitive advantage, particularly in sectors with high product return rates like fashion and electronics.
Impact of Reverse Logistics on Supply Chain Management
1. Cost Management:
- Operational Costs: Effective reverse logistics can help manage costs associated with returns, recycling, and disposal. By optimizing these processes, companies can reduce operational expenses and improve overall cost efficiency.
- Inventory Costs: Managing returns and refurbishments effectively can help control inventory levels, preventing overstock situations and reducing carrying costs.
2. Customer Satisfaction and Retention:
- Return Policies: A streamlined reverse logistics process enhances customer satisfaction by making returns and exchanges hassle-free. This is crucial for maintaining customer loyalty and encouraging repeat business.
- Service Quality: Efficient handling of returns and repairs contributes to a positive customer experience, which is essential for retaining customers and building a strong brand reputation.
3. Operational Efficiency:
- Streamlined Processes: Implementing effective reverse logistics processes helps in the smooth handling of returns, recalls, and repairs. This efficiency can lead to quicker turnaround times and reduced lead times in processing returns.
- Resource Optimization: Recycling and repackaging reduce the need for new materials and products, leading to better resource utilization and lower production costs.
Importance in Sectors with High Return Rates
1. Fashion Industry:
- High Return Rates: The fashion industry experiences high return rates due to size, fit, and style issues. Efficient reverse logistics systems are crucial for managing these returns effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: Fashion retailers that excel in handling returns can offer more attractive return policies, enhancing customer satisfaction and gaining a competitive edge. Companies like Zara and ASOS leverage efficient reverse logistics to quickly process returns and restock items.
2. Electronics Industry:
- Complex Returns: The electronics sector faces challenges with returns due to product defects, compatibility issues, and customer dissatisfaction. Efficient reverse logistics is essential for managing repairs, refurbishments, and recycling of electronic products.
- Brand Loyalty: Electronics companies that provide effective repair and refurbishment services can build stronger brand loyalty and trust. Companies like Apple and Dell use reverse logistics to manage returns and offer refurbishments, contributing to customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Importance of Reverse Logistics to Your Business
Reverse logistics is integral to modern supply chain management, offering numerous benefits that enhance customer experience, foster brand loyalty, and contribute to overall operational efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at how reverse logistics impacts a business:
Enhancing Customer Experience
Streamlined Returns and Exchanges: Efficient reverse logistics simplifies returns and exchanges, making the process convenient and quick for customers, which enhances their shopping experience and reduces frustration.
Customer Support and Satisfaction: Responsive customer support and effective management of returns and repairs ensure high-quality products and improve customer satisfaction, building trust in the brand.
Fostering Brand Loyalty
Positive Customer Experience: Generous return policies and effective handling of returns and repairs help differentiate the brand, encouraging repeat business and fostering loyalty through positive experiences.
Consistency and Reliability: Reliable management of returns and repairs reinforces trust and loyalty, as consistent, dependable service strengthens customer relationships and enhances brand reputation.
Cost Savings
Reverse logistics contributes to cost savings by improving operational efficiency and managing inventory effectively. Streamlined returns and recycling processes reduce handling costs and minimize expenses related to defective or unsellable products. Properly managed returns also help in maintaining optimal inventory levels, reducing overstocking and associated storage costs. Furthermore, refurbishing and reselling returned items generate additional revenue, recovering value from products that would otherwise be discarded, leading to overall financial benefits for the company.
Resource Recovery
Reverse logistics supports resource recovery by enabling the recycling and reuse of materials from returned or end-of-life products. This process involves reclaiming valuable components and materials, such as metals and plastics, which can be repurposed for new manufacturing. By reusing these resources, companies can reduce their reliance on virgin raw materials, lower production costs, and minimize waste. This not only helps in managing inventory effectively but also contributes to a more sustainable and cost-efficient supply chain.
Environmental Benefits
Reverse logistics plays a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability by reducing waste and supporting eco-friendly practices. Through efficient recycling and proper disposal of products, businesses can minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills and decrease their overall environmental footprint. By aligning with regulatory requirements and focusing on sustainability, companies contribute to a circular economy, where products and materials are continuously reused and recycled, ultimately supporting broader environmental goals and reducing the impact on natural resources.

Challenges in Reverse Logistics
Cost Management:
Managing the costs associated with reverse logistics, including return processing, recycling, and disposal, can be complex and expensive. Handling returns involves costs for transportation, inspection, and restocking, while recycling and disposal require additional resources. Balancing these costs with the need to maintain customer satisfaction can be a significant challenge.
Resource Allocation:
Allocating resources effectively in reverse logistics is crucial but challenging. Companies need to manage labor, facilities, and equipment for handling returns, repairs, and recycling. Ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently without causing bottlenecks or service delays requires careful planning and coordination.
Operational Inefficiencies:
Inefficiencies in reverse logistics processes, such as delays in processing returns or errors in handling repairs, can lead to increased operational costs and diminished customer satisfaction. Inefficient processes can also result in higher rates of returned inventory, increased waste, and lower overall productivity.
Complexities in global supply chains:
Global supply chains introduce additional complexities in reverse logistics. Variations in regulations, language barriers, and logistical challenges across different countries can complicate the return and disposal processes. Managing returns across borders also involves dealing with diverse customs regulations, transportation issues, and varying levels of infrastructure quality.
Mitigating Challenges through Strategic Planning and Technological Investments
Strategic Planning:
Businesses can mitigate reverse logistics challenges by developing comprehensive return policies and efficient processes tailored to their needs. Strategic planning involves forecasting return rates, optimizing return flows, and designing streamlined processes for handling returns and recycling. Implementing clear guidelines and performance metrics helps in managing costs and resource allocation effectively.
Technological Investments:
Investing in technology can significantly improve reverse logistics operations. Advanced tracking systems and data analytics tools provide real-time visibility into return processes, enabling better decision-making and faster processing. Automation technologies, such as robotics and automated sorting systems, can enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Additionally, software solutions for managing inventory and processing returns can help streamline operations and reduce errors, leading to overall improved performance and cost savings.
Best Practices for Effective Reverse Logistics
1. Investing in Data Analytics:
Leveraging data analytics can greatly enhance reverse logistics by providing insights into return patterns, costs, and process inefficiencies. By analyzing data on return rates, reasons for returns, and customer feedback, companies can identify trends and areas for improvement. This allows for more informed decision-making, better forecasting of returns, and targeted strategies to reduce return rates and costs.
2. Refining Return Policies:
Developing clear, customer-friendly return policies is essential for managing returns effectively. Policies should be straightforward, easy to understand, and designed to minimize friction for customers. Implementing features like pre-paid return labels, flexible return windows, and hassle-free exchanges can improve customer satisfaction and streamline the return process.
3. Partnering with Third-Party Logistics Providers:
Collaborating with third-party logistics (3PL) providers who specialize in reverse logistics can enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness. 3PL providers bring expertise in managing returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal and can offer scalable solutions tailored to specific needs. They also often have established networks and technology solutions that can improve logistics performance and reduce operational burdens.

Role of Automation and AI
1. Automation:
Automation plays a crucial role in optimizing reverse logistics by streamlining various processes. Automated sorting systems, robotics, and conveyor belts can speed up the processing of returned goods, reducing manual handling and processing times. Automated inventory management systems help track returned items more accurately, ensuring efficient restocking or processing.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI enhances reverse logistics by providing advanced predictive analytics, optimizing returns management, and improving decision-making. AI algorithms can predict return trends, detect anomalies in return patterns, and recommend process improvements. Machine learning models can also automate decision-making in return approvals, repairs, and refurbishment processes, leading to faster and more accurate handling of returns.
Future Trends in Reverse Logistics
1. Increasing Focus on Sustainability:
The growing emphasis on sustainability is driving significant changes in reverse logistics. Companies are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing waste and enhancing recycling processes. The focus on minimizing environmental impact is leading to the development of more efficient waste management systems and increased investment in sustainable materials. This trend aligns with broader corporate social responsibility goals and consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices.
2. Circular Supply Chains:
Circular supply chains are gaining traction as businesses seek to create closed-loop systems where products and materials are continually reused and recycled. This approach minimizes waste, conserves resources, and reduces environmental impact. Reverse logistics plays a critical role in circular supply chains by facilitating the return, repair, refurbishment, and recycling of products. Companies are implementing strategies to extend product lifecycles and create more sustainable business models through circular economy principles.
3. Growing Use of Blockchain:
Blockchain technology is increasingly being used to enhance transparency and traceability in reverse logistics. By providing a secure and immutable record of transactions, blockchain can improve the tracking of returned goods, ensure compliance with environmental regulations, and reduce fraud. It enables better visibility into the entire supply chain, allowing companies to verify the authenticity and condition of returned products, streamline processes, and build trust with customers and partners.
4. Expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT):
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming reverse logistics by enabling real-time tracking and monitoring of products throughout their return journey. IoT devices and sensors can provide valuable data on the condition and location of returned items, improving the accuracy of inventory management and processing. Enhanced visibility through IoT allows for better decision-making, faster processing times, and more efficient management of reverse logistics operations.
Impact of Environmental Regulations and Green Initiatives
1. Stricter Environmental Regulations:
As governments and regulatory bodies implement stricter environmental regulations, companies will need to adapt their reverse logistics practices to ensure compliance. Regulations regarding waste disposal, recycling standards, and emissions are likely to become more stringent, pushing businesses to adopt greener practices and technologies. Compliance with these regulations will require investments in sustainable practices and innovative solutions for waste management and recycling.
2. Green Initiatives and Consumer Demand:
Growing consumer awareness and demand for sustainable products and practices are shaping the future of reverse logistics. Businesses are increasingly focusing on green initiatives, such as reducing carbon footprints, using recyclable materials, and minimizing packaging waste. This shift towards sustainability is driving companies to enhance their reverse logistics processes to align with environmental goals and meet consumer expectations. Companies that embrace these green initiatives can gain a competitive edge and build stronger relationships with environmentally conscious customers.
The Bottom Line
Reverse logistics is increasingly vital in global supply chains, focusing on the logistics process of managing product returns, recycling, and disposal. As businesses strive for process optimization, reverse logistics becomes essential for improving efficiency and reducing costs. Effective resource allocation ensures that labor, facilities, and technology are utilized effectively to handle returned goods and recover valuable materials. Integrating advanced logistics solutions such as IoT and blockchain enhances visibility and traceability, further optimizing reverse logistics operations.
